The twin-engine Tu-104, which made its first flight in 1955, symbolized the start of the global civil jet. The Tu-104 was derived from the Tupolev Tu-16 jet bomber, first flown in 1952. So it is the developed version of the Tu-16. This aircraft was a stepping stone in the history of commercial aviation for the USSR providing sustained passenger jet service.
Read More: Fall of TU-144, Tupolev TU144, the Soviet supersonic aircraft
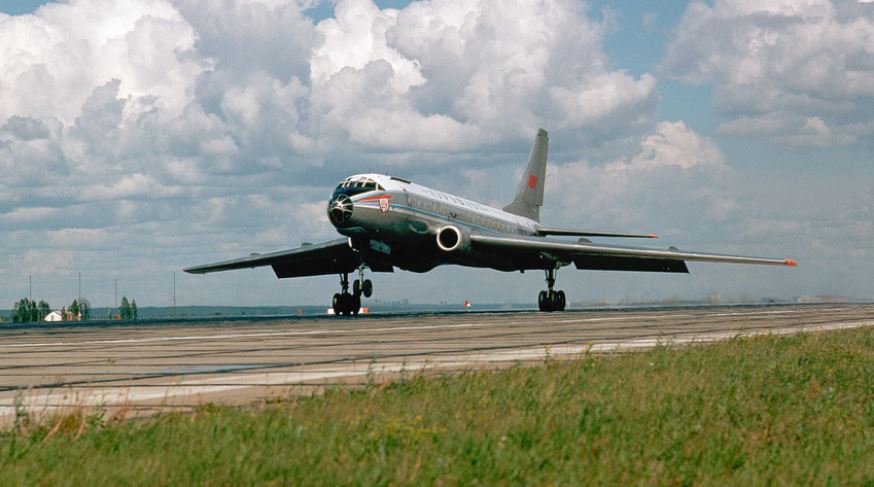

Tupolev TU-104
World War II stimulated a significant increase in international flying airplanes. The value of the aircraft was recognized, and production increased to meet the soaring demand from the government for planes. Today, we are in the time of the world of jets. Jet engines are more reliable, safer, and cheaper to operate than piston engines. They produce enormous thrusts for their weight. So, they can fly faster than piston-powered aircraft. While mentioning jets, Tupolev is the name not to be missed.
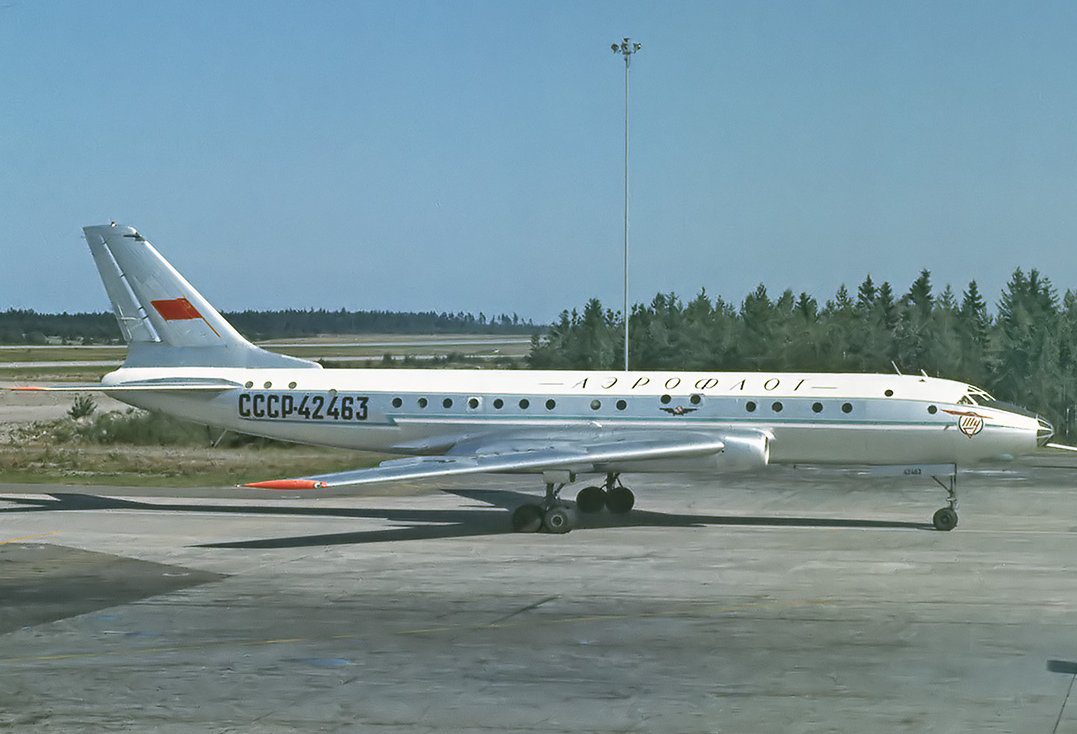

Tupolev, officially ANTK A.N. Tupolev, is a soviet aerospace design bureau civilian passenger airliner that produces the bulk of civilian and military bombers. The company was established in September 1922. Tt developed the Soviet’s first commercial jet airliner and the world’s first supersonic passenger jet aircraft. Tupolev Tu-104 is the 2nd pioneer of this glorious jet age, one of the most advanced aircraft of its time, which, in fact, is the father in the post-war civil aviation in the USSR and the entire communist part of the world. Tu-104 represents the first soviet commercial jet aviation and one of the first jet airliners in the world; the Tu-104 was the pride of the Soviet Union.

As the Soviet Union possessed vast territory with a total of 10 time zones across the country, Jet airliners were a genuine requirement.
The Tupolev Tu-104 was a narrow-body Soviet turbo-jet carrier. It was the second jet to enter regular service, behind the British-made commercial jet de Havilland Comet. The Tupolev Tu-104 was operating solely globally from 1956 to 1958 when the British jetliner was laid off the rock bottom per safety concerns.
Read More: The new Russian turboprop IL114-300 and its scope
The highly innovative British-made aircraft, the world’s first jet airliner, which was de Havilland DH.106 Comet, traveled faster and higher than propeller aircraft. It was much quieter and smoother and had stylish blended wings which possessed jet engines that were hidden. Its first regular flight commenced on May 2nd, 1952.
Two years later, the Comet’s initial career came to an end, following two accidents in an exceeding row which was the consequence of metal fatigue causing the fuselage to burst apart during flight. Until all the circumstances were made clear, the airliner was prohibited from making further flights by Churchill. USSR grabbed the opportunity to become the country with its carrier, starting the development in 1954 A.D. They built the advanced jet engine after the Brits were unsure of the further flight scheduling of de Havilland Comet 4.

In the early 1950s, the Soviet-bound Aeroflot faced similar problems as other airlines worldwide faced similar issues. Piston engines were becoming reckless, and there was a rise in maintenance costs of aircraft, and flights were time-consuming, which reduced the profitability of airlines. Aeroflot was required to create up to something that would be much more efficient than unreliable piston-engine aircraft of the time.
The Soviet Union-run Aeroflot airline needed a sophisticated airliner that had a higher capacity and performing ability than the piston-engine powered airplane in terms of operation. Soon, the design request for such an airliner was permeated by the Tupolev OKB by basing their new airliner on its Tu-16 ‘Badger’ jet bomber. Tupolev retained a lot of the design features from the Tu-16 and transferred them to the Tu-104. The wings, engines, power plant, plumage, and tail surfaces of the Tu-16 were without variations from Tu-104.
Still, the new design was incorporated to encompass a wider, pressurized fuselage with seating to accommodate 50 passengers. The low wing was attached to the new jet instead of the mid-wing. A new long fuselage would be used for the Tu-104, which was Albeit. Tupolev retained a lot of the design features from the Tu-16 and transferred them to the Tu-104. As the productions and design were present, the Soviets could decrease the costs to a significant rate.
Following main requirements were appraised for the new commercial jet by Tupolev:
1. Capacity to undertake between 25.000 and 30.000 flight hours
2. Seating of about 50-100 passengers
3. Fly at a speed between 460 – 500 miles per hour
An initial design accommodating 50 passengers was presented by Tupolev, which could be extended to 70 seats. Soon after the approval to build a long-range passenger jet-powered carrier was given by the USSR government, the new jet was designated as the Tu-16P by the council.
Subsequently, it became the Tu-104, with the four meaning it was a passenger aircraft. Later, Tupolev assigned the number 4 to the passenger-carrying airplane. In precisely two years’ interval, Tu-104 was prepared for its first test flights, performed by captain Y.T. Alasheev and his first officer B.M. Timoshenko in 1955. The bureau statistics confirmed that the Tu-104 had a well-made and luxurious design. The test results satisfied the council of ministers within the USSR, leading to further Tu-104 production approval.
On the other hand, the appearance of the Tu-104 created quite a stir in the aviation and general public on the Western side. It became imminent that the Soviet Agency had accomplished the pinnacle of success by mastering the complex technologies of the aircraft industry. It demonstrated that the USSR had made a huge step forward in modern civil jet airplanes. The 1st unit of Aeroflot was introduced on September 15th, 1956. The initial scheduled service took place between Moscow and Irkutsk. Following this, international flights commenced to Prague. A total of 201 units of the Tu-104 were built between the time 1956 and 1960.
How is Tu-104 interior ?
As passenger experience is one of the foremost priorities of airlines, commercial jets should work on specific styles of passenger seats, baggage compartments, sides. Tupolev Tu-104 interior features must ensure comfort to passengers while remaining lightweight to reduce consumption of fuel. With the development of the Tu-104, more priority was accorded to the interior design of aircraft. Comfortable seats and hot meals with fresh drinks were provided to the passengers. Air conditioning system, electrical appliances of preparation and heating of passenger meal, cabin radio, lighting salons, etc., were accounted to Tupolev Tu-104 interior.

The initial version of the-104 accommodated 50 passengers, which had 29 airframes. The improved version of Tu-104A extended its seating capacity to 70; the advancement continued with Tu-104B occupying a seat of 115, with new navigation, radio, and flight equipment. The other variant of Tu-104D possessed a VIP version comprising two sleeper cabins forward and a 39 seat cabin aft. A later version of Tu-104V seated 115 passengers by decreasing seat pitch and adding seat rows.

Another Tu-104B airframe was rebuilt for 115 passengers, adding up new radio and navigational equipment. Similarly, Tu-104SH had two versions of Navigator trainer.
Cockpit
Cockpit means the space or the compartment set aside in control of an aircraft., A modernized aircraft’s cockpit must give all of the information necessary for the crew to evaluate the aircraft’s performance and act appropriately as it is the interface between aircraft and crew.
Read More: Russian Airlines ‘Aeroflot’ likely to enter Nepal

The Tu-104, with big engines inducted in the wing roots next to the cabin, was noisy and prone to vibrations. Pilots obtained the preliminary information from their external environment on the earliest powered flight days. In the 1950s, many instruments were introduced on tu-104 cockpit which would enable aircraft to land in poor weather. Indicators, instruments, and electromechanical controls were equipped on every surface of on tu-104 cockpit, which was within the pilot’s reach and walls of on tu-104 cockpit. Instrument panels possessing the main instruments were arranged in front of the pilot panels and on tu-104 cockpit.

Subsequently, the consecutive use of the Tu-104 exemplified that the aircraft was sensitive to stalling at low speed. Tu-104 has poorly controlled during flight. The new generation of jetliners made the aircraft obsolete. The Tu-104 was not a perfect aircraft, but it paved the path for new generations of jet aircraft, Tu-154 for taking an example as a beginner in the civil jet airline. Like the Comet, the Tu-104 encountered a series of incidents that led to its demise.

The last flight for Aeroflot occurred on March 17th, 1979, when one of its units couldn’t take off due to shifting cargo. Upcoming refinements learned from their mistakes rectified the jetliner over the years. Although the unimpressive number of air carriers and the serial number of accidents, the Tu-104 offered regular service for a couple of decades. The Tu-104 encouraged further jet breakthroughs in eventual years.
The air transport industry, the sphere of commerce, utilizes aircraft to transport passengers, cargoes, mails, etc. The air transport industry comprises civil and general aviation. With the advent of new technologies, aircraft have been used to advance the cause of humanity. Aircraft are perceived as tools to counterpoint the lives of people worldwide in the face of technological, economic, and political challenges.