Update on VOR/DME installation at Dhangadhi and Chandragadhi Airport
May 5, 2017
Dhangadhi and Chandragadhi Airport is a busiest domestic airport serving in trunk route. Dhangadhi airport is also being upgraded to an international airport, being Nepal’s fourth international airport.
Dhangadhi and Chandragadhi airport are likely to be developed thoroughly. The airport which had aircraft fuel depot installed recently will now have VOR/DME installed in its vicinity. The VOR/DME instrument will be installed at airports in Chandragadi in the East likewise in west at Dhangadhi Airport.
The instruments are aimed to be installed within January 2018. Some Japanese engineers were on the airport to check the feasibility of installation at late 2016.
The Chandragadhi Airport has applied the application to CAAN to acquire 6 Bighas of Land at East Side towards Runway 26 to install the VOR/DME station, noted airport source. The installation work of VOR/DME is handed over to the Japan International Cooperation Agency – JICA the Japanese Company.
-About VOR/DME Instruments:-
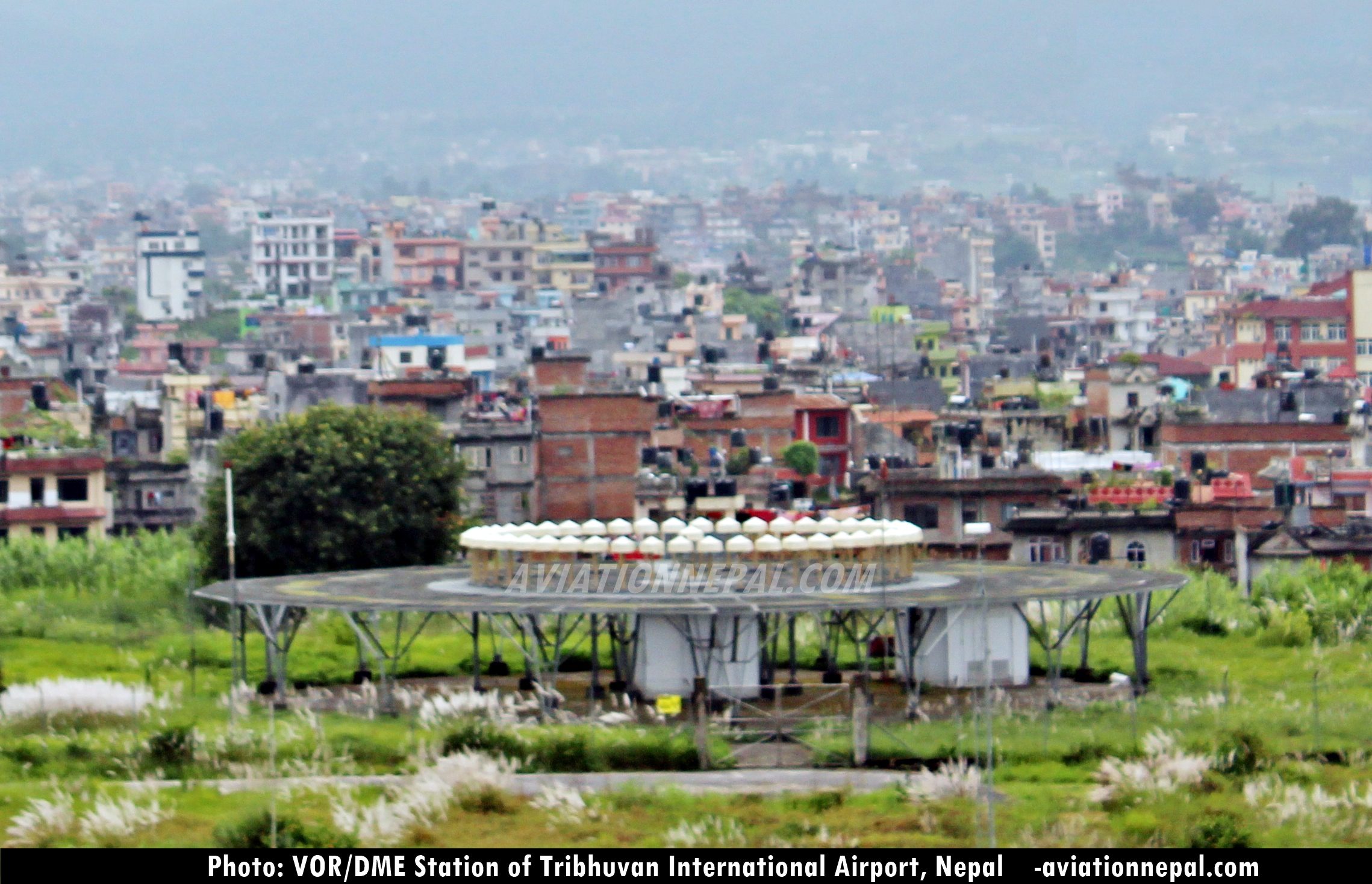
VOR/ DME are the radio navigation system. VOR (VHF Omnidirectional Radio Range) provides the angle between aircraft and station (usually Airport) and DME (Distance Measuring Equipment) gives the distance between aircraft and the station. The VOR DME equipment produces radio beacon in 360 degrees while aircraft receives those radio beacon.
VOR/DME is the combined radio navigation station for an aircraft which includes two of radio beacons placed together. A VHF (Very High Frequency) omnidirectional range (VOR) and the distance measuring equipment (DME) are combined together.
The VOR was first invented back around in 1950s but it only came into operation after the introduction of low-cost solid state receivers in the 1960s. DME was a modification of World War II-era navigation systems like Gee-H which came to development in 1946. Alike VOR, DME also came on operation with the introduction of solid state receivers during 1960s.
VOR produces an angle between the station and the receiver in the aircraft. Similarly DME does the same for range. They together provide the two measurements needed to produce a navigational “fix” using a chart.
VOR/DME has eventually won the standardization effort due to a number of merit factors. One was that the direct measurement systems like Loran were generally much more expensive to implement while Decca had problems with static interference from lightning strikes because of its low 70 to 129 kHz frequency.
The hybrid VOR/DME was used largely which was easier rather than to plot on a map. VOR/DME measurement from a signal station reveals an angle and range which can easily be plotted on the chart. Using a system based on two-angles, as an example, requires two measurements at different frequencies (or using two radios) and then the angles plotted from both on a single chart, which may be difficult in a confined cockpit.
DME stands for Distance Measuring Equipment. This system is used as an interrogator in the aircraft and a transponder on the ground at the VOR system. DME shows the relative ground speed toward the station and note the actual ground speed of the aircraft, which happens only when flying toward or from the station. DME distance is called slant range and this is the result of horizontal distance and altitude of the aircraft. Slant range becomes altitude when flying exactly overhead of the DME.
DME is used with IFR procedures, ILS approaches, and as a distance tool for position reporting, flying a constant arc (at a certain distance/DME). VFR rated pilots can use the DME system too, if the aircraft has the proper equipment installed.
Aircraft normally use DME to determine their distance from a land-based transponder by sending and receiving pulse pairs – two pulses of fixed duration and separation. The ground stations are typically allocated with VORs or ILS systems. A low-power DME can be collocated with an ILS glide slope antenna installation where it provides an accurate distance to touchdown function, similar to that otherwise provided by ILS marker beacons.
Typical Distance measuring equipment, ground transponder system for en-route or terminal navigation will have a 1 kW peak pulse output on the assigned UHF channel.
In context of Nepal, there are five VOR/DME stations in operation which are as follows:
- VOR/DME Kathmandu (Frequency: 113.2 MHz / 79X, Location: 274025 N 0852055 E)
- VOR/DME Nepalgunj (Frequency: 115.1 MHz / 98X, Location: 280605 N 0813903 E)
- VOR/DME Simara (Frequency: 112.9 MHz / 76X, Location: 270951 N 0845856 E)
- VOR/DME Biratnagar (Frequency: 114.1 MHz / 88X, Location: 262858 N 0861458 E)
- VOR/DME Bhairahawa (Frequency: 114.7 MHz / 94X, Location: 273012 N 0832558 E)