Air transport is one of the most popular means of transportation that sees an average of one hundred thousand commercial flights daily. More than 2 million people take to the skies daily for business or leisure. Despite large air traffic daily, flying is the safest way to travel. Air traffic controllers of any nation perform diligent work of directing aircraft on the ground and providing advisory services to aircraft to keep passengers and crew members safe. What are the various roles of air traffic controllers in aviation?
Before diving straight into the roles of air traffic controllers, it is crucial to know what air traffic and air traffic control mean.

Air traffic
Air traffic refers to the number of airplanes flying in an area or operating in the maneuvering area of an airport. Airports and airfields accommodate the air traffic, dictate the aircraft types for usage, and provide various services, including regular public transport, charters, cargo, flight training, military services, etc. With the rise in air demand, effectively handling an increased air traffic volume at airports requires a systematic set of air traffic control principles.
Also Read: Life as an Air Traffic Controller
Air traffic control
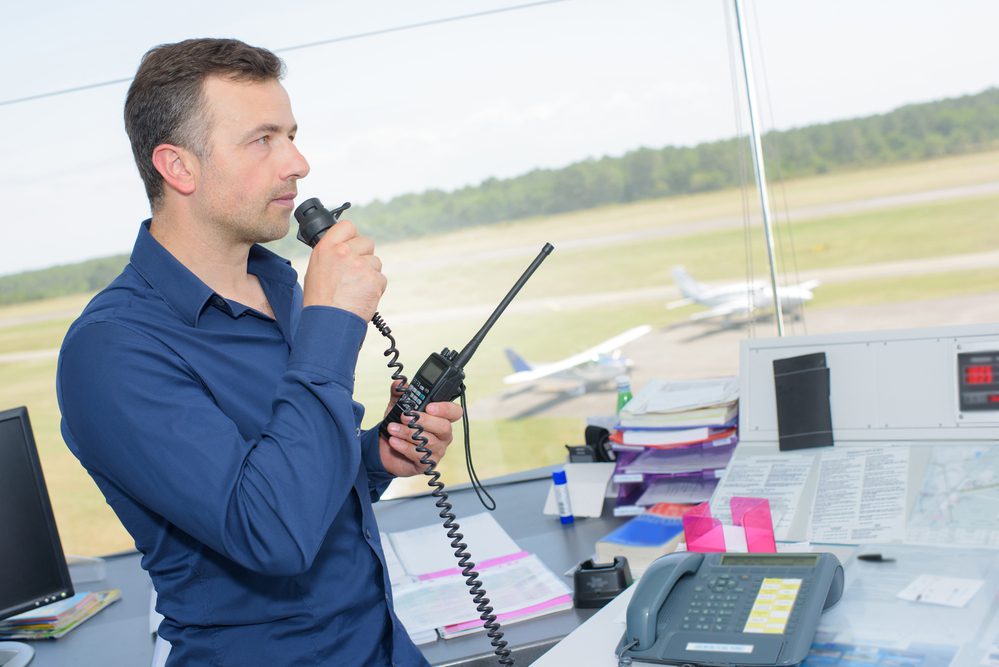
Air traffic control is a ground-based service in airports that includes air-ground communication, prevention of collision, orderly flow of air navigation of airplanes through the local airspace, direction for takeoff and landings, etc. Air traffic control service is more common in busier aerodromes of airports to ensure safe departure and secure arrival of all flights with minimal delay. In air traffic control, a separation rule exists to keep aircraft outside a minimum distance from another aircraft or from a block of airspace. The separation depends on the class of airspace the aircraft is flying and the flight rules under which an aircraft can be flown. This rule results in the remote risk of aircraft collision and avoidance of wake turbulence created by a preceding aircraft.

Air traffic controllers and their roles in aviation
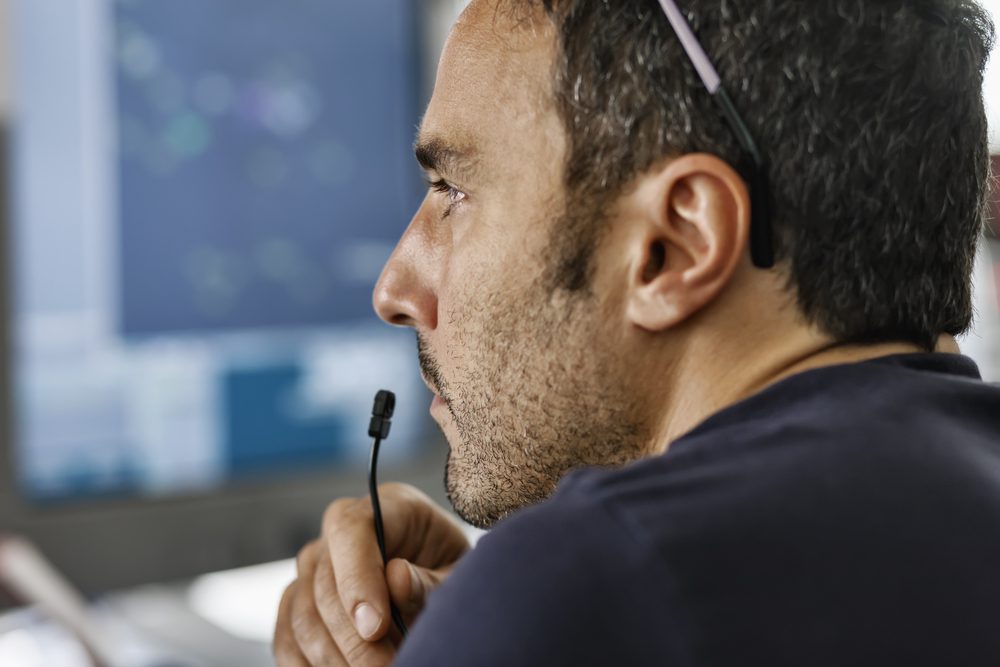
Most major airports, which handle large passenger and cargo movements, have an Air Traffic Control (ATC) service to control every single movement at the airport and facilitate the safe and expeditious flow of air traffic. Air traffic control centers and control towers in airports are well-recognized symbols of air safety providing air traffic control services for coordinating takeoffs, landings, ground traffic, and aircraft. Usually stationed in these facilities are Air Traffic Controllers who take responsibility for the safe operations of commercial and private aircraft. They monitor the position, speed, and altitude of airplanes, give clearance for aircraft to take off and land safely and apply separation rules to ensure safe distances are maintained between aircraft.
As skies do not have traffic lights, air traffic controllers aid in coordinating air movements, advise and update pilots about nearby planes and provide direction around and through turbulent weather. They keep in radio contact with the flight crew and issue instructions that pilots are required to obey.
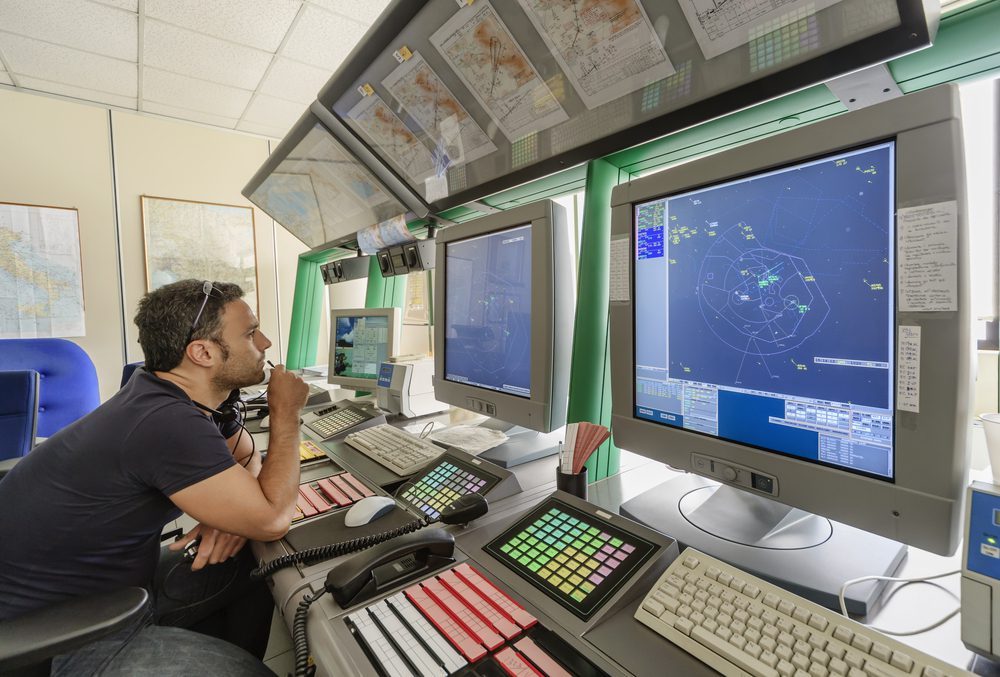

They carry out work in stressful environments, with no room for error, utilizing the precise and effective application of rules and procedures. Air traffic controllers act as pilots’ second pair of eyes to help accomplish passengers’ demands for safe and on-time journeys. The areas surrounding airports can rest in knowing that air controllers will keep air traffic flowing smoothly with very little margin for aerial crashes.
Break down of air traffic controller workforce
Roles of air traffic controllers are varied depending on their areas of service, which include:
1. Aerodrome control service
Aerodrome control service deals with aircraft on the ground or in the vicinity of the aerodrome. It includes giving clearance to land and take off and handling all movements within the airport terminal control area. The aerodrome controllers work in a control tower and manage traffic within 5 miles of the airport. Located in the airport having regularly scheduled flights, the aerodrome control service provides guidance to flight crews regarding correct taxi positions on stands and runways to keep orders in a busy environment.

2. Approach control service/Terminal control
The approach control service links the aerodrome control and the area control and focuses on air traffic control service for arriving and departing controlled flights. The approach controllers have a specific task to control planes on approach to an airfield, guide them through a sequence of locations to land, and ensure departing traffic is kept clear of arrivals. A specific duty is to give radar directions to planes to line them up with the runway and also provide separation between arriving and departing traffic. Approach controllers manage the approaching aircraft, instruct aircraft that just took off, and monitor the flight’s climb, descent, and approach phases.
The terminal control center is assigned airspace boundaries and altitudes, varying by the airport’s size, traffic flows (departures, arrivals, and overflights), and terrain.
3. Area control service
Area controllers provide service to aircraft traveling between airports and issue clearances and instructions for airborne aircraft. They track and guide aircraft flying at higher elevations through a sector and ensure it is properly separated from all other aircraft in the immediate area. Controlling and monitoring movement between origin and destination airports, they instruct departing aircraft to climb to their assigned altitude and approaching aircraft to meet altitude restrictions. The main responsibility of area controllers is assigning cruising levels, dealing with crossing traffic, and maintaining separation during the final climb and initial descent. Once the aircraft leaves its airspace and continues on a flight, crossing a defined geographical area, they hand off the responsibility for controlling the aircraft to the next en-route center controllers.
Step-by-step role of air traffic controllers
Air traffic controllers follow aircraft maintenance management solutions and systems to safely direct and navigate airplanes. Air traffic controllers perform their roles in a phased manner following a typical flight profile. It involves:
• Preflight
During this phase, the pilot files a flight plan with the tower, including airline name, flight number, aircraft type, equipment, intended airspeed, and flight route. The air traffic control tower reviews the weather and flight-plan information and gives clearance to the pilot for the flight’s route.
• Takeoff and departure
Once the air traffic control tower gives the clearance to lift off the ground, the pilot powers up the aircraft and speeds down the runway. This procedure is known as takeoff. The ground controller directs the pilot to get the plane out of the gate area and instructs him on which way to taxi and which runway to go to for takeoff. Once the plane reaches the designated takeoff runway, the strip is handed over to the local controller, who gives the pilot final clearance for takeoff.
The plane is said to have departed when the plane lifts off the ground, climbs to a cruising altitude, and flies five miles beyond the airport. As the plane takes off, the local controller ensures the maintenance of a safe distance between planes and provides the new radio frequency for the departure controller. Now it is the departure controllers’ job to monitor aircraft electronically and communicates with the pilot.

• In the air
The departure controller at the TRACON (Terminal Radar Approach Control) facility monitors the aircraft during the ascent to the en-route portion before passing it off to a center controller. Once the plane leaves TRACON airspace, it enters a sector of the Air Route Traffic Control Center (ARTCC), which is a radar system supervising flights within the area. The center controller is in charge of all air-to-ground communication and must provide the pilot with updated weather and air-traffic information and information regarding speed and altitude to maintain the safe separation of aircraft.
• Descent
As the pilot descends and maneuvers the aircraft 50 miles from the destination airport, it is within TRACON airspace. The oversight is given to the approach controller, who directs the pilots to adjustments in heading, speed, and altitude to line up and prepare to land.
• Approach and landing
During the approach, the pilot aligns the aircraft with the designated landing runway and the approach controller fuses several streams of descending the plane into one even pace. If the plane is 10 miles away from the runway, it is the local controller’s job to do the needful at this phase.
The local controller checks the runways and skies above the runways, and if everything is safe, it gives clearance for landing and directs pilots through taxiways before finally passing the plane off to the ground controller.

How do airports without ATC service control their air traffic?
Several airfields and aerodromes in the world do not have ATC service to control every single airport at the airport for every departure and arrival. In case you are wondering how to control air traffic without ATC service, there are strict procedures and regulations for pilots to follow and separate themselves from other traffic.
Under standard procedures, pilots make their transmissions on CTAF-Common Traffic Advisory Frequency broadcasting callsign, flight rules, aircraft type, departure and destination aerodromes, and taxi & departure intentions. This will include aware other pilots in uncontrolled airports.